Expert tendonitis treatment in Chicagoland
You have more than 4,000 tendons in your body. They connect muscles to bones and are a vital part of every movement you make. When you experience pain with movement, you may have an irritated and inflamed tendon – tendonitis (also known as tendinitis). At Advocate Health Care, our orthopedic and sports medicine specialists will sort out the cause and help you on the path to recovery.
Schedule an orthopedic appointment
From recent injuries to nagging aches and pains, our orthopedic specialists can help. Schedule your orthopedic appointment in LiveWell, online or by phone.
What is tendonitis?
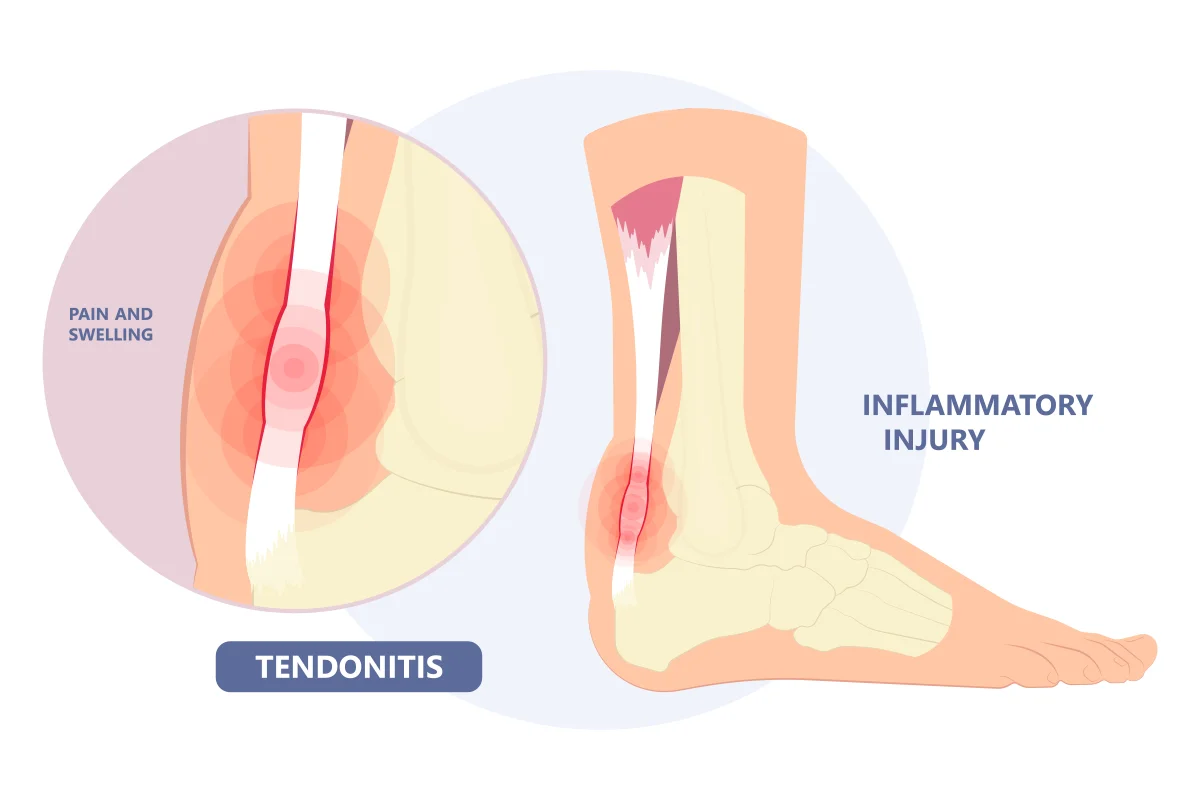
Tendonitis – inflammation of a tendon – can affect any tendon, but it’s usually found in the shoulders, elbows, wrists, thumbs, hips, knees, or ankles. It can be chronic or acute.
Chronic tendonitis is the most common kind. It’s usually caused by overuse or repetitive movements in sports, work, or day-to-day activities. Chronic tendonitis can also be caused by conditions like arthritis. It develops gradually and gets worse over time.
Acute tendonitis appears suddenly and is usually the result of an injury. If a person doesn’t get treatment, their acute tendonitis can become chronic.
Can tendonitis heal on its own?
Tendonitis won’t heal completely on its own. However, there are self-care measures you can use that may help with tendon pain and make symptoms go away. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation are very effective for tendonitis:
- Rest the sore tendon
- Apply ice or a cold pack
- Use an elastic bandage to compress the injury
- Elevate the affected body part above the level of the heart if possible
Prompt treatment is important. Leaving tendonitis untreated can lead to complications such as tendinosis (degeneration of tendon tissue) or a tendon rupture (tearing of tendon tissue).
Tendonitis symptoms
Tendonitis symptoms occur at the spot where the tendon is inflamed. They include:
- Pain or aching
- Redness
- Swelling and warmth
- Tenderness
Tendonitis causes
Causes of tendonitis include:
- Repetitive motions: Athletes who play sports like golf, tennis, and baseball are at high risk for sports injuries like tendonitis. People whose jobs require repetitive motions or standing all the time are also at risk.
- Improper technique or overuse: Using the wrong technique or worn-out equipment when exercising or doing other physical activities can lead to tendonitis. In addition, playing sports infrequently can stress the tendons and cause tendonitis.
- Certain medical conditions: Arthritis or other disorders may put stress on your tendons, leading to tendonitis.
Your risk of tendonitis is also increased if you’re older than 40. Tendons become less flexible with age, so they become injured more easily.
Types of tendonitis
Different types of tendonitis have specific names. Some of the types that affect the arms and hands are:
- Bicep tendonitis: Affects tendons of the upper arms.
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis: Affects the thumbs and wrists.
- Elbow tendonitis: When it affects the outside of the lower arms and elbows, it’s called lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow. When it affects the inside of the lower arms and elbows, it’s called medial epicondylitis, golfer’s elbow or pitcher’s elbow.
- Extensor tendonitis: Affects tendons that allow fingers to extend.
- Shoulder impingement: Affects tendons of the shoulder and is also called swimmer’s shoulder. Causes shoulder pain.
Some common types of tendonitis that affect the lower legs are:
- Achilles tendonitis: Affects the Achilles tendons at the back of the ankles.
- Patellar tendonitis: Affects patellar tendons of the knees and causes knee pain.
- Peroneal tendonitis: Affects peroneal tendons on the outsides of lower legs.
- Posterior tibial tendonitis: Affects posterior tibial tendons on the insides of lower legs.
Tendinitis diagnosis
When you see your doctor about your possible tendonitis symptoms, they’ll perform a physical exam that may include:
- Discussion of your symptoms and medical history
- Physical exam to look for common signs of tendonitis, like a thickened tendon or limited joint movement
- X-rays, if needed, to rule out other causes of the pain
Your doctor will explain treatment options and work with you to plan treatments that meet your goals for recovery.
Expert tendonitis treatment
For most tendonitis injuries, our doctors and sports medicine specialists recommend nonsurgical options like the following:
- Rest: Avoid using the tendon or immobilize it with a splint, sling, or crutches.
- Medications: Use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen to relieve inflammation and pain.
- Corticosteroid injections: Relieve pain with injections. We recommend these injections only for short-term use.
- Physical therapy: Our skilled orthopedic physical therapists recommend exercises to strengthen tendons and provide treatments to reduce inflammation. Your treatment will be tailored to your sport and specific needs.
If these methods don’t work well enough, we may suggest surgery for some injuries. As much as possible, we use minimally invasive surgery, which uses small incisions and specially designed tools to minimize scarring and recovery time.
Surgery for tendonitis varies depending on which tendon is affected. Tendonitis surgery may involve realigning tendons, removing damaged tissue, or removing bone spurs that may be putting pressure on tendons.
Get care
We help you live well. And we’re here for you in person and online.