Urinary tract infection (UTI): symptoms, causes & treatment
Find a urologistA urinary tract infection or UTI is a common infection that can occur in any part of your urinary system. The urinary system includes your urethra, the two tubes that transport urine into the bladder (ureters), the bladder and kidneys. Most UTIs develop in the lower urinary tract, affecting the bladder and urethra.
UTIs can be uncomfortable and annoying but are typically not threatening to your health. These infections become a concern if they move into the kidneys. Women are more likely to develop UTIs than men with 10% of females reporting having a UTI at least once per year.
Get relief from a UTI with a video visit with your virtual primary care or in-person provider. Or visit an immediate care center to see an Advocate Health Care urology expert.
Need care now? Try telehealth
Symptom Checker can help you find the right type of care based on your symptoms. From 24/7 urgent care video visits to e-visits, we’ll recommend the best visit for you. Try Symptom Checker in LiveWell.
Is a UTI an STI?
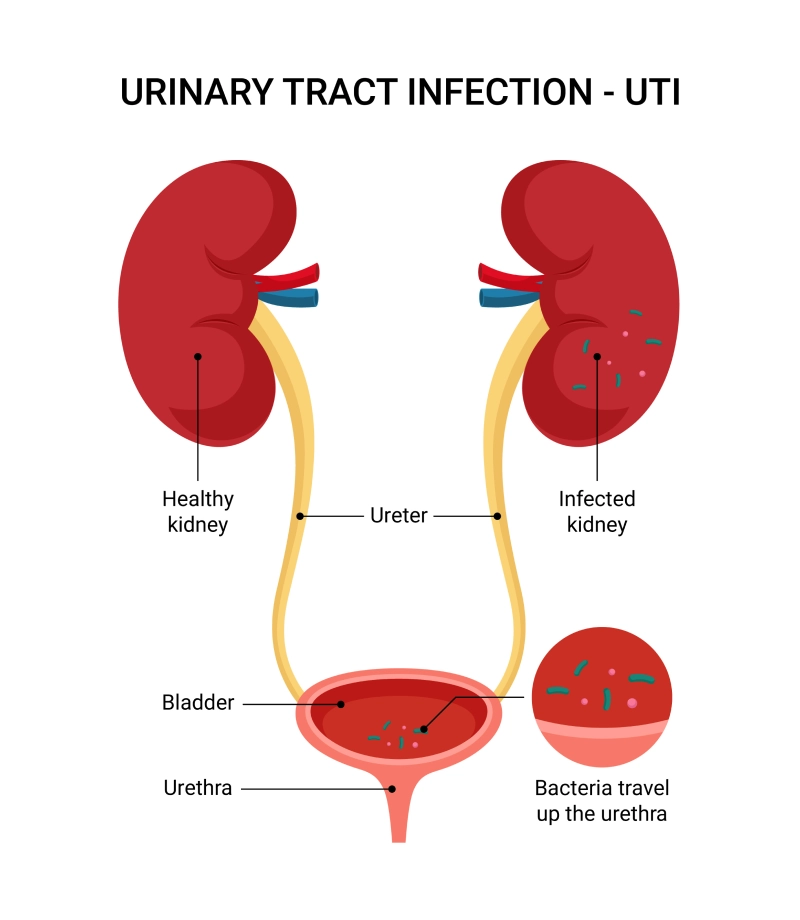
When you have a urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteria may move through the urethra to the bladder and kidneys, leading to an infected kidney or bladder.
No, a UTI is not considered a sexually transmitted infection (STI). A UTI is typically caused by bacteria that enters the urinary tract, usually through the urethra. While sexual activity can increase your risk of developing a UTI, UTIs are not transmitted through sexual contact like STIs are.
STIs are infections caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites that are spread primarily through sexual contact, while UTIs are infections of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra or kidneys.
However, it's important to note that symptoms of a UTI, such as a burning sensation when you urinate, can overlap with certain STIs. See your doctor to rule out an STI.
How does a UTI make you feel?
A UTI can affect you all over your body. The most noticeable sign of a UTI is pain or burning when you urinate, which often feels like a sharp, stinging sensation. This is also a common sign of some STIs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea.
You may also have to go to the bathroom frequently, and your urine could look cloudy and have a strong smell to it. Lower back pain is also normal if you have a UTI.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) symptoms
You could experience some or all of these UTI symptoms:
- Burning during urination
- Urine that appears cloudy
- Feeling a sense of urgency to urinate, even when you don’t have to
- Urinating often in small amounts at a time
- Urine with a strong odor
- Pelvic discomfort in women – especially in the center of the pelvis
- Blood in your urine
- Rectal pain in men
Urinary tract infection (UTI) types
You may experience varying UTI symptoms depending on which area of the urinary system is infected.
Bladder (cystitis)
The most common type of UTI, also known as a bladder infection, may cause frequent and uncomfortable urination. You may also experience pelvic pressure and lower belly pain.
Urethra (urethritis)
A lower urinary tract infection causing inflammation of the urethra. Common symptoms include a discharge or a burning sensation or pain with urination.
Kidney (pyelonephritis)
If the infection spreads to your kidneys, it can lead to serious health problems. Symptoms of a kidney infection can include back or side pain, a fever over 100 degrees, chills or hot flashes, headache and nausea.
Contact your doctor if you’re experiencing any symptoms of a UTI.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) causes
Urinary tract infections are commonly caused by bacteria entering the urinary system through the urethra, then multiplying and spreading. A majority of UTI causes can come from E.coli bacteria, which is found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Human anatomy is also one of the main UTI causes. About four times as many females experience UTIs than males due to a woman’s urethra being shorter, making it closer to the anus and easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract. While UTIs in men are less frequent, they still can occur.
Women going through menopause are more likely to experience UTIs. This is because of lower estrogen levels, which affects the urinary tract and makes it easier to get infected. Menopause can also weaken your body’s ability to fight an infection and increase your risk of getting a UTI.
You may be more at risk of developing a UTI if you:
- Are sexually active
- Use a diaphragm as birth control or spermicides
- Have diabetes
- Are pregnant
- Are postmenopausal
- Have any condition such as kidney stones that block the ureter
Urinary tract infection (UTI) diagnosis
Our experienced Advocate Health Care specialists will discuss your possible UTI symptoms with you and take a urine sample for testing. A urinalysis will test for bacteria and red and white blood cells in your urine to help indicate if there is an infection.
If you experience frequent UTIs, your doctor may order a urine culture to determine what type of bacteria is in your urine, or a cystoscopy, a procedure where a scope is inserted into the bladder to get a better look at what’s causing the problem.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) treatment
After diagnosis, your doctor will work with you to find the best UTI treatment option based on the type of infection, your medical history and current health. Most urinary tract infections can be treated with a course of UTI antibiotics.
If you experience frequent UTIs, your doctor may recommend a longer course of antibiotics. You may feel better after one to two days of taking antibiotics for UTIs, but you should always finish the full course as directed.
It usually takes about seven days for the bacteria causing the infection to clear out of your system. If the full course of antibiotics isn’t taken, the infection may come back again or spread.
In more serious cases, you may need to spend some time in the hospital where we can provide IV antibiotics and round-the-clock care to prevent any permanent damage to your kidneys.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) prevention
You can help lower the risk of getting UTIs by:
- Urinating before and after sexual activity
- Wiping from front to back after urination or bowel movements
- Drinking more fluids, especially water
- Taking showers instead of baths
- Using unscented feminine hygiene products
Some studies show that cranberries help prevent infection-causing bacteria from attaching to the walls of the urinary tract. Adding unsweetened cranberry juice, cranberry supplements or dried cranberries to your diet may reduce your risk of getting a urinary tract infection.
Get care
We help you live well. And we’re here for you in person and online.